import torchTensor Basic
Ref
Book: 딥러닝 파이토치 교과서(서지영 지음, 길벗 출판사)
github: https://github.com/gilbutITbook/080289/tree/main
Basic
print(torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]]))tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])print(torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]],device="cuda:0"))tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]], device='cuda:0')print(torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]],dtype=torch.float64))tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]], dtype=torch.float64)- ndarray 변환
temp = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(temp.numpy())[[1 2]
[3 4]]temp = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]],device="cuda:0")
print(temp.to("cpu").numpy())[[1 2]
[3 4]]- 텐서 차원 조작
temp = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])temp.shapetorch.Size([2, 2])temp.view(4,1)tensor([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]])temp.view(-1)tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])temp.view(1,-1)tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4]])temp.view(-1,1)tensor([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]])모델 정의
- nn.Module() 상속하여 정의
class MLP(Module):
def __init__(self, inputs):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.layer = Linear(inputs,1) # 계층 정의
self.activation = Sigmoid() # 활성화 함수 정의
def forward(self, X):
X = self.layer(X)
X = self.activation(X)
return X- Sequential 신경망 정의하는 방법
import torch.nn as nn
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2))
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=30, kernel_size=5),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2))
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=30*5*5, out_features=10, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
def forward(self,x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = x.view(x.shape[0],-1)
x = slelf.layer3(x)
return x
model = MLP() # 모델에 대한 객체 생성
모델의 파라미터 정의
- 손실 함수 (loss function)
\(y\)와 \(\hat y\)의 오차를 구해서 모델의 정확성을 측정
BCELoss: 이진 분류
CrossEntropyLoss: 다중 클래스 분류
MSELoss: 회귀 모델
- 옵티마이저 (optimizer)
데이터의 손실 함수를 바탕으로 모델의 업데이트 방법 결정
torch.optim.Optimizer(params, defaults)는 옵티마이저 기본 클래스zero_grad()옵티마이저 사용된 파라미터의 기울기 0으로torch.optim.lr_scheduler에폭에 따라 학습률 조절종류
<optim Adadelta, optim.Adagrad, optim.Adam, optim.SparseAdam, optim.Adamax>
<optim.ASGD, optim.LBFGS>
<optim.RMSProp, optim.Rprop, optim.SGD>
모델 훈련
- 예시 코드
for epoch in range(100):
yhat = model(x_train)
loss = criterion(yhat, y_train)
optimizer.zero_gard()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()예시
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inlinedataset = pd.read_csv('car_evaluation.csv')dataset.head()| price | maint | doors | persons | lug_capacity | safety | output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | small | low | unacc |
| 1 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | small | med | unacc |
| 2 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | small | high | unacc |
| 3 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | med | low | unacc |
| 4 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | med | med | unacc |
- output(차상태): unacc(허용 불가능한 수준), 양호(good), 매우 좋은(very good, vgood)
dataset.head()| price | maint | doors | persons | lug_capacity | safety | output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | small | low | unacc |
| 1 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | small | med | unacc |
| 2 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | small | high | unacc |
| 3 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | med | low | unacc |
| 4 | vhigh | vhigh | 2 | 2 | med | med | unacc |
fig_size = plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]
fig_size[0] = 8
fig_size[1] = 6
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = fig_size
dataset.output.value_counts().plot(kind='pie', autopct='%0.05f%%', colors=['lightblue', 'lightgreen', 'orange', 'pink'], explode=(0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0.05))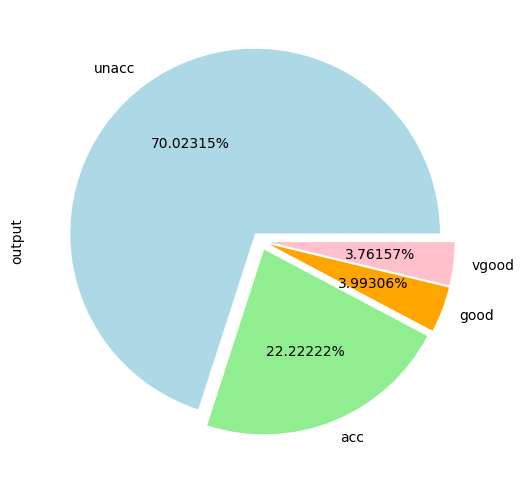
categorical_columns = ['price', 'maint', 'doors', 'persons', 'lug_capacity', 'safety']for category in categorical_columns:
dataset[category] = dataset[category].astype('category')- astype() 메서드를 이용하여 데이터를 범주형으로 변환
- 범주형 데이터를 텐서로 변환하기 위해서는
범주형 데이터 -> dataser[category] -> 넘파이 배열(NumPy array) -> 텐서(Tensor)
price = dataset['price'].cat.codes.values
maint = dataset['maint'].cat.codes.values
doors = dataset['doors'].cat.codes.values
persons = dataset['persons'].cat.codes.values
lug_capacity = dataset['lug_capacity'].cat.codes.values
safety = dataset['safety'].cat.codes.values
categorical_data = np.stack([price, maint, doors, persons, lug_capacity, safety], 1)
categorical_data[:10]array([[3, 3, 0, 0, 2, 1],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 1, 2],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 2],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[3, 3, 0, 1, 2, 1]], dtype=int8)- 배열 텐서로 변환
categorical_data = torch.tensor(categorical_data, dtype=torch.int64)
categorical_data[:10]tensor([[3, 3, 0, 0, 2, 1],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 1, 2],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 2],
[3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[3, 3, 0, 1, 2, 1]])- 레이블(outputs) 사용할 칼럼을 텐서로 변환
outputs = pd.get_dummies(dataset.output)
outputs = outputs.values
outputs = torch.tensor(outputs).flatten()
print(categorical_data.shape)
print(outputs.shape)torch.Size([1728, 6])
torch.Size([6912])note: revel(), reshape(), flatten()
텐서 차원 변경
categorical_column_sizes = [len(dataset[column].cat.categories) for column in categorical_columns]
categorical_embedding_sizes = [(col_size, min(50, (col_size+1)//2)) for col_size in categorical_column_sizes]
print(categorical_embedding_sizes)[(4, 2), (4, 2), (4, 2), (3, 2), (3, 2), (3, 2)]- test/train
total_records = 1728
test_records = int(total_records * .2) # 20%만 테스트 용도로 사용
categorical_train_data = categorical_data[:total_records-test_records]
categorical_test_data = categorical_data[total_records-test_records:total_records]
train_outputs = outputs[:total_records-test_records]
test_outputs = outputs[total_records-test_records:total_records]print(len(categorical_train_data))
print(len(train_outputs))
print(len(categorical_test_data))
print(len(test_outputs))1383
1383
345
345- 네트워크 생성
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_size, output_size, layers, p=0.4):
super().__init__()
self.all_embeddings = nn.ModuleList([nn.Embedding(ni, nf) for ni, nf in embedding_size])
self.embedding_dropout = nn.Dropout(p)
all_layers = []
num_categorical_cols = sum((nf for ni, nf in embedding_size))
input_size = num_categorical_cols
for i in layers:
all_layers.append(nn.Linear(input_size, i))
all_layers.append(nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
all_layers.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(i)) # 배치정규화.. 평균0 분산 1
all_layers.append(nn.Dropout(p))
input_size = i
all_layers.append(nn.Linear(layers[-1], output_size))
self.layers = nn.Sequential(*all_layers)
def forward(self, x_categorical):
embeddings = []
for i,e in enumerate(self.all_embeddings):
embeddings.append(e(x_categorical[:,i]))
x = torch.cat(embeddings, 1)
x = self.embedding_dropout(x)
x = self.layers(x)
return xmodel = Model(categorical_embedding_sizes, 4, [200,100,50], p=0.4)
print(model)Model(
(all_embeddings): ModuleList(
(0-2): 3 x Embedding(4, 2)
(3-5): 3 x Embedding(3, 2)
)
(embedding_dropout): Dropout(p=0.4, inplace=False)
(layers): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=12, out_features=200, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): BatchNorm1d(200, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(3): Dropout(p=0.4, inplace=False)
(4): Linear(in_features=200, out_features=100, bias=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
(6): BatchNorm1d(100, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(7): Dropout(p=0.4, inplace=False)
(8): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=50, bias=True)
(9): ReLU(inplace=True)
(10): BatchNorm1d(50, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(11): Dropout(p=0.4, inplace=False)
(12): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=4, bias=True)
)
)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device('cuda')
else:
device = torch.device('cpu')epochs = 500
aggregated_losses = []
train_outputs = train_outputs.to(device=device, dtype=torch.int64)
for i in range(epochs):
i += 1
y_pred = model(categorical_train_data)
single_loss = loss_function(y_pred, train_outputs)
aggregated_losses.append(single_loss) # 반복할 때마다 오차 aggregated_losses에 추가
if i%25 == 1:
print(f'epoch: {i:3} loss: {single_loss.item():10.8f}')
optimizer.zero_grad()
single_loss.backward() # 가중치 업데이트
optimizer.step() # 기울기 업데이트
print(f'epoch: {i:3} loss: {single_loss.item():10.10f}')test_outputs = test_outputs.to(device=device, dtype=torch.int64)
with torch.no_grad():
y_val = model(categorical_test_data)
loss = loss_function(y_val, test_outputs)
print(f'Loss: {loss:.8f}')print(y_val[:5])y_val = np.argmax(y_val, axis=1)
print(y_val[:5])
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
print(confusion_matrix(test_outputs,y_val))
print(classification_report(test_outputs,y_val))
print(accuracy_score(test_outputs, y_val))